Understanding the Role of a Videographer
Definition of a Videographer
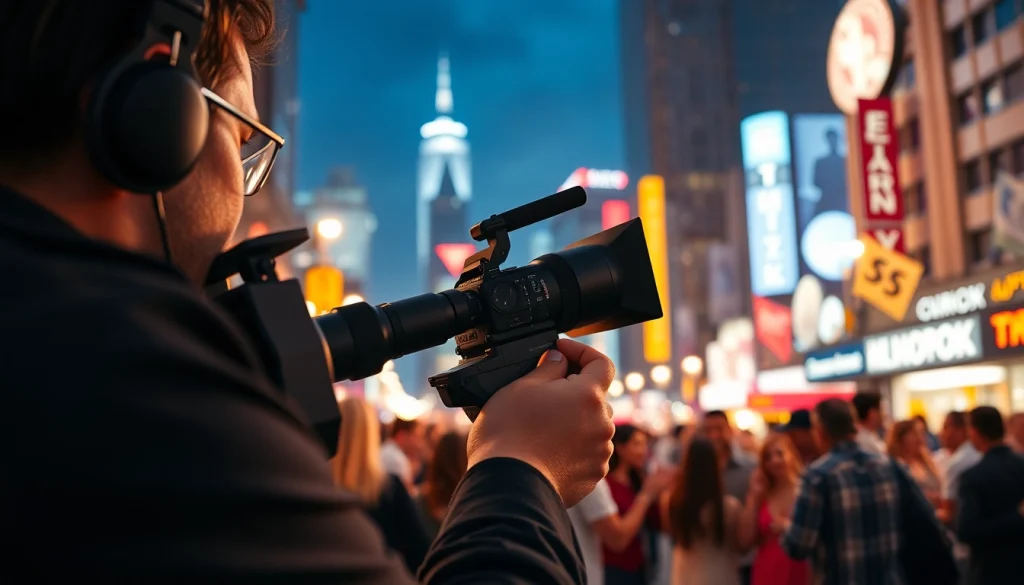
A Videographer is a creative professional specializing in capturing moving images, as well as sound, to create engaging visual narratives. This profession blends artistry with technology and is vital across various fields, including film, television, corporate communication, and event documentation. Videographers utilize their skills to tell stories, convey ideas, and capture moments that resonate with audiences.
Key Responsibilities
Videographers wear many hats, often encompassing a wide array of responsibilities in their projects:
- Planning: Pre-production planning includes brainstorming concepts, scouting locations, and developing shooting schedules.
- Filming: On-set, they oversee camera operation, manage lighting, and ensure optimal audio capture.
- Editing: Post-production involves selecting the best footage, cutting it into a coherent sequence, and adding effects, sound, and music.
- Collaboration: Often, videographers work closely with directors, producers, and clients to achieve a unified vision.
- Marketing: Maintaining an online portfolio and promoting their services to attract new clients.
Skills Required to Succeed as a Videographer
Success in videography demands a blend of creative talent and technical prowess. Here are essential skills every videographer should possess:
- Technical Skills: Proficiency in operating camera equipment, understanding lighting techniques, and working with sound recording devices.
- Editing Software Knowledge: Familiarity with tools like Adobe Premiere Pro, Final Cut Pro, or DaVinci Resolve is crucial for post-production work.
- Storytelling Ability: Crafting a compelling narrative that engages viewers is at the heart of effective videography.
- Attention to Detail: A keen eye for elements such as framing, composition, and continuity helps in creating polished final products.
- Communication Skills: Clear communication with clients and team members is essential for achieving project goals.
Types of Videography Services Offered
Cinematic Videography
Cinematic videography is characterized by its artistic approach, often resembling a film production. This style includes:
- Story-Driven Content: It emphasizes narratives, often using professional actors and scripted dialogue.
- High Production Value: This type utilizes advanced equipment, staging, and special effects, requiring precise planning and execution.
- Commercial Projects: Companies frequently employ cinematic styles for advertisements, promotional videos, or brand storytelling.
Event Videography
Event videography captures key moments of various gatherings such as weddings, corporate events, or concerts. Its defining features include:
- Live Coverage: Constantly adapting to spontaneous moments while ensuring critical events are well-documented.
- Editing Highlights: Producing concise highlight reels that summarize longer events for easy sharing and viewing.
- Client Interaction: Understanding client preferences to tailor the final product closely to their desires.
Corporate Videography
Corporate videography serves businesses through a variety of formats, including corporate training videos, promotional materials, or internal communications. Key aspects include:
- Brand Consistency: Ensuring that all videos align with the company’s brand identity and messaging strategies.
- Training and Development: Creating instructional videos aimed at employee skill-building and corporate culture reinforcement.
- Client Engagement: Leveraging imagery and storytelling to create a connection with target demographics.
Essential Equipment for Videographers
Cameras and Lenses
The choice of equipment significantly impacts the outcome of a videographer’s work. Essential components include:
- Cameras: High-definition cameras, such as DSLRs or mirrorless systems, are commonly used for their versatility and image quality.
- Lenses: Different lenses (wide-angle, telephoto, and prime lenses) create various effects and viewpoints essential for storytelling.
- Stabilization Gear: Equipment like gimbals or steadicams ensures smooth motion during filming.
Audio and Lighting Gear
Quality audio and lighting equipment are indispensable for professional videography:
- Microphones: A variety of microphones (lapel, shotgun) capture crisp sound and are crucial for dialogue and ambient noise.
- Lighting Kits: Softboxes, LEDs, and reflectors help control lighting conditions, ensuring that subjects are adequately illuminated.
- Windshields: To improve audio capture in outdoor settings, windshields help eliminate distracting background noise.
Editing Software and Tools
The post-production phase utilizes various software tools essential for creating a cohesive final product:
- Video Editing Software: Programs like Adobe Premiere Pro and Final Cut Pro are standard in the industry for their robust features.
- Color Grading Tools: Software such as DaVinci Resolve allows for color correction and grading to elevate the visual appeal.
- Sound Editing Software: Tools like Adobe Audition help refine audio by removing noise and enhancing clarity.
Building a Portfolio as a Videographer
Showcasing Your Best Work
Creating a compelling portfolio is crucial for attracting clients. Here are strategies to build an effective one:
- Diverse Projects: Include a variety of styles and formats that demonstrate your range as a videographer.
- Quality Over Quantity: It’s better to showcase fewer high-quality pieces than to include many mediocre works.
- Update Regularly: Continuously refresh your portfolio with recent projects to reflect evolving skills and trends.
Networking with Clients
Establishing strong client relationships is key for sustained success:
- Attending Industry Events: Engage in film festivals, workshops, or corporate gatherings to meet potential clients and collaborators.
- Online Presence: Building a professional website and active social media accounts showcases your work and engages potential clients.
- Client Follow-ups: Maintain communication post-project to cultivate relationships and encourage referrals.
Marketing Strategies for Videographers
Effective marketing increases visibility and client acquisition:
- SEO Optimization: Implement search engine optimization strategies to enhance your online visibility in search results.
- Content Marketing: Creating blog posts or videos that provide value can attract potential clients and establish authority.
- Social Media Advertising: Leverage platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and YouTube to share reels or highlight important projects to reach a larger audience.
Trends and Future of Videography
Impact of Technology on Videography
Technology is rapidly transforming videography, affecting both how projects are created and consumed:
- 4K and 8K Resolution: Advancements in camera technology have made ultra-high-definition filming more accessible for commercial use.
- Drone Videography: Drones provide unique aerial perspectives, enhancing storytelling in various contexts, from events to real estate.
- Mobile Videography: The capability to capture high-quality video on smartphones is changing content creation and broadening accessibility.
Emerging Styles and Techniques
Videographers must stay updated on current trends to remain competitive:
- Live Streaming: Real-time broadcasting for events is increasingly popular and offers immediate engagement with audiences.
- Interactive Videos: Utilizing technology that allows viewer interaction places the audience at the center of the experience.
- Virtual Reality and 360° Filming: These immersive techniques create unique storytelling opportunities that engage viewers differently.
How to Adapt to Industry Changes as a Videographer
Continual learning and adaptation are essential for thriving in a fast-evolving landscape:
- Education and Training: Regularly attending workshops or pursuing online courses can enhance skills and keep up with new technology.
- Community Engagement: Joining professional networks allows videographers to share experiences and learn from each other.
- Feedback Integration: Actively seeking client feedback helps refine techniques and messaging, ensuring relevance in a changing market.