Understanding Steel Fabrication
What is Steel Fabrication?
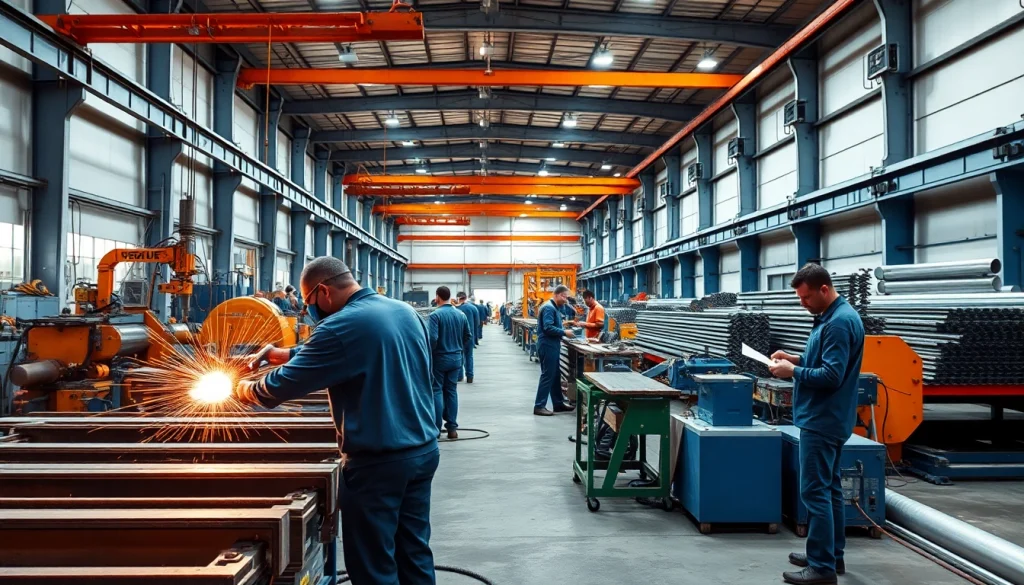
Steel fabrication refers to the process of constructing and assembling metal structures through the cutting, bending, and shaping of steel materials. This critical aspect of industrial production plays a pivotal role in various sectors, including construction, machinery, and shipbuilding. The goal of steel fabrication is to create components and structures that meet specific customer requirements while upholding high-quality standards for durability and performance.
In a steel fabrication shop, skilled artisans utilize advanced machinery alongside traditional craftsmanship techniques to transform raw steel into engineered parts. This process encompasses a broad range of activities, including welding, machining, and finishing, underscoring the versatility and significance of steel fabrication in modern manufacturing.
History and Evolution of Steel Fabrication
The history of steel fabrication can be traced back to the early days of metallurgy. Initially, metals were fashioned manually, but as industrialization took hold in the late 18th century, the need for more sophisticated tools and methods emerged. The introduction of the Bessemer process in the mid-19th century revolutionized steel production, significantly lowering costs and boosting availability.
With the advancements in processes and technologies, steel fabrication expanded. By the early 20th century, technologies such as electric arc welding and the use of structural steel became commonplace, shaping the skyline of modern cities. The rise of skyscrapers and complex infrastructures highlighted the crucial role of steel fabrication in construction, showcasing its capacity to withstand immense stress and load.
Different Types of Steel Used in Fabrication
Understanding the types of steel used in fabrication is vital. The primary categories include:
- Carbon Steel: Most commonly used for structural applications due to its strength and ductility. It comes in various grades depending on the carbon content.
- Alloy Steel: This type is composed of additional elements, such as chromium and nickel, which enhance specific properties like toughness and wear resistance.
- Stainless Steel: Renowned for its corrosion resistance, stainless steel is frequently utilized in environments where oxidation is a concern.
- Tool Steel: Known for its hardness and ability to retain shape at high temperatures, tool steel is typically used for cutting and drilling equipment.
Each type possesses unique characteristics that influence their applicability in different environments and projects.
The Process of Steel Fabrication in the Shop
Designing Fabrication Plans
The first step in steel fabrication involves detailed planning. Fabrication plans serve as blueprints, outlining dimensions, materials, and processes necessary to complete a project. Modern steel fabrication shops often utilize computer-aided design (CAD) software to create precise and adaptable design plans. This technology allows for rapid adjustments and simulations, ensuring a high degree of accuracy in the final outcome.
Collaboration between project managers, engineers, and clients is essential during this stage. Engaging with all parties helps align expectations and fosters clear communication, ultimately contributing to the success of the project.
Machining Techniques in Steel Fabrication Shop
After the design is finalized, the next phase is executing the plans through various machining techniques. The most common methods include:
- Cutting: Methods such as plasma cutting, laser cutting, and waterjet cutting enable precise cuts that minimize waste and improve efficiency.
- Bending: Machines like press brakes are employed to bend steel to required angles, enabling complex shapes to be formed without compromising structural integrity.
- Welding: Welding joins pieces of steel through methods such as MIG, TIG, and arc welding, ensuring robust connections.
- Finishing: This includes processes such as grinding, polishing, and painting, which enhance the durability and aesthetic of the final product.
Quality Control Standards in Steel Fabrication
Quality assurance is the backbone of any reputable steel fabrication shop. Rigorous testing and inspection protocols ensure that fabricated products meet industry standards and customer specifications. Common practices include:
- Material Inspection: Before materials enter the shop, they undergo checks to confirm their compliance with relevant standards.
- Dimensional Checks: Regularly measuring components during production to ensure they adhere to specified tolerances is vital for maintaining quality.
- Weld Testing: Welds are typically inspected through non-destructive testing methods like ultrasonic and radiographic testing to ensure integrity.
- Final Inspection: A meticulous review is conducted pre-shipment to guarantee that every item meets the expected quality and specification.
Essential Equipment in a Steel Fabrication Shop
Overview of Common Machinery
A state-of-the-art steel fabrication shop is equipped with various machinery that plays a significant role in enhancing productivity and quality. Core equipment includes:
- Plasma Cutters: Used for high-speed cutting of metal sheets with precision.
- Welding Machines: Varied types facilitate different welding techniques to meld steel components.
- Press Brakes: Essential for bending metal sheets into desired angles and shapes.
- Shears: Employed for efficiently cutting large sheets of metal without distortion.
- Milling Machines: Necessary for shaping and altering materials by removing excess steel.
Safety Equipment and Protocols
Ensuring a safe working environment is paramount in a steel fabrication shop. Safety protocols must be stringently observed to protect all personnel involved. Critical safety equipment includes:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Items such as helmets, gloves, safety goggles, and hearing protection minimize injury risks.
- Emergency Equipment: Fire extinguishers, first aid kits, and eye wash stations should be readily accessible throughout the facility.
- Training Programs: Regular training sessions on safe equipment operation and the handling of hazardous materials equip employees with essential knowledge.
Innovative Tools Transforming Steel Fabrication
The evolution of technology has significantly impacted the steel fabrication industry. Innovations that are reshaping modern fabrication shops include:
- Advanced Robotics: Robots are increasingly integrated into fabrication processes for welding, cutting, and assembly, enhancing speed and precision while reducing the need for human intervention.
- 3D Printing: This technology offers rapid prototyping and production capabilities, allowing for the creation of complex parts without the traditional constraints of machining.
- IoT Devices: The Internet of Things is being utilized for real-time monitoring of machinery and operations, optimizing workflow and predictively maintaining equipment to avoid downtime.
Common Challenges in Steel Fabrication
Raw Material Sourcing Issues
The reliance on international supply chains for raw materials can lead to challenges in availability and pricing stability. Fluctuating costs and potential delays can significantly affect project timelines. To mitigate these issues, it is crucial for fabrication shops to establish strong relationships with multiple suppliers, enabling better negotiation and flexibility in sourcing materials.
Workforce Skill Gaps
The rapid advancements in technology and machinery have resulted in a growing skill gap within the workforce. Many experienced workers are retiring, leaving behind vacancies that require specialized skills. To combat this, shops should invest in training and apprenticeship programs aimed at cultivating a skilled workforce prepared to meet modern demands.
Environmental Regulations Impacting Operations
As regulations surrounding environmental impacts become more stringent, steel fabrication shops must comply with strict guidelines regarding waste management, emissions, and energy consumption. Implementing green practices such as recycling scrap metal and utilizing energy-efficient machinery can not only ensure compliance but also enhance corporate responsibility and appeal to eco-conscious clients.
Future Trends in Steel Fabrication
Automation and Robotics in Steel Fabrication Shops
The integration of automation and robotics in steel fabrication shops is no longer a trend but a requirement for maintaining competitiveness. Automated systems can streamline production processes, resulting in greater efficiency, reduced human error, and lower labor costs. As technology continues to advance, the capabilities of automation will further expand, allowing for more complex tasks to be handled without human intervention.
Green Initiatives in the Steel Industry
The push for sustainability is transforming the steel industry. Fabrication shops are increasingly adopting green initiatives, such as using recycled materials, reducing waste, and optimizing energy use. Developing a reputation as an environmentally responsible operation can attract more clients and foster loyalty among those committed to sustainable practices.
Emerging Technologies Shaping the Future
Technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning are beginning to reshape how fabrication shops operate. These technologies can optimize workflow, predict maintenance needs, and improve overall productivity. As they become more accessible, integrating such technologies will be essential for future-proofing businesses against emerging industry challenges.